CAMO transfers the motion from the source 2D video to the target 3D mesh.
Abstract
Motion transfer from 2D videos to 3D assets is a challenging problem, due to inherent pose ambiguities and diverse object shapes, often requiring category-specific parametric templates. We propose CAMO, a category-agnostic framework that transfers motion to diverse target meshes directly from monocular 2D videos without relying on predefined templates or explicit 3D supervision. The core of CAMO is a morphology-parameterized articulated 3D Gaussian splatting model combined with dense semantic correspondences to jointly adapt shape and pose through optimization. This approach effectively alleviates shape-pose ambiguities, enabling visually faithful motion transfer for diverse categories. Experimental results demonstrate superior motion accuracy, efficiency, and visual coherence compared to existing methods, significantly advancing motion transfer in varied object categories and casual video scenarios.
Method
Our goal is to transfer articulated motion from a monocular video to arbitrary 3D characters. We take as input a static 3D target mesh $\mathcal{M}^{tgt}$ and a source monocular RGB video with paired foreground masks $\{I_t, M_t\}_{t=0}^T$, where $I_t$ is a frame from time $t$, and $M_t$ is obtained via off-the-shelf segmentation model (Kirillov et al., 2023). We aim to produce a temporally coherent sequence of deformed meshes $\{\mathcal{M}^{tgt}_t\}_{t=0}^T$ that faithfully reproduces the source motion.
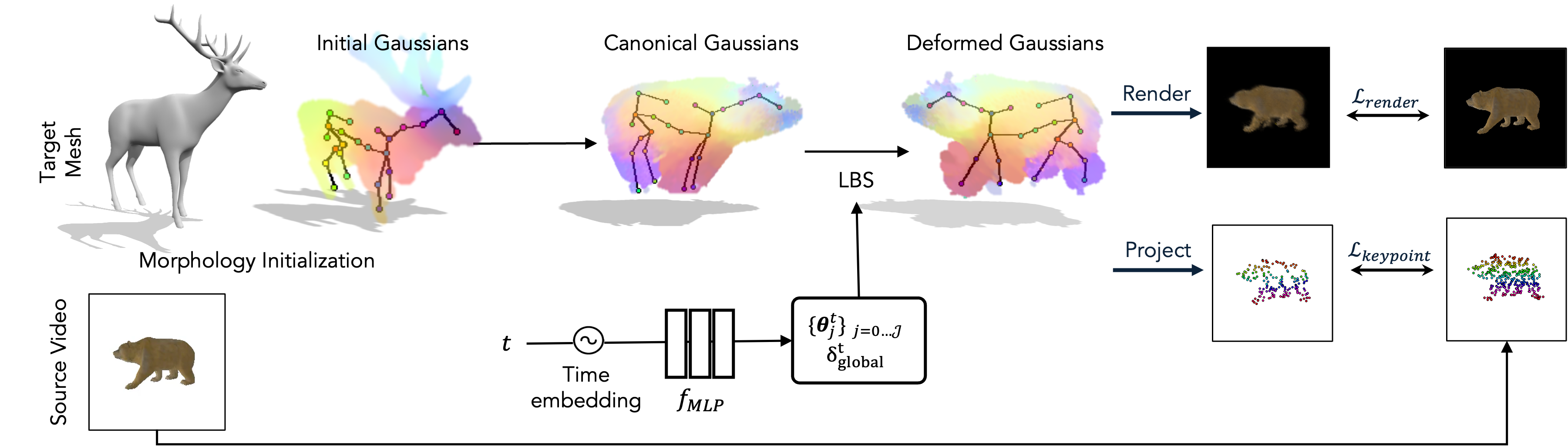
We first encapsulate the target mesh with an Articulated-GS (Yao et al., 2025) representation with pose parameters (Sec. 3.1). We then parameterize morphology using learnable bone lengths, a global scale, and local Gaussian offsets (Sec. 3.2). This representation disentangles shape variation from pose dynamics. Finally, all shape and pose parameters are optimized jointly via differentiable rendering and dense semantic correspondences (Sec. 3.3–3.4), yielding semantically coherent motion aligned to the source.
During optimization, the morphology-adaptive shape parameters and motion field are iteratively updated to recover the target’s shape and pose from the frames.
Results
2D-to-3D Motion Transfer
CAMO handles diverse motions across objects with differing morphologies—including variations in body proportions and volumes—enabling high-fidelity 2D-to-3D motion transfer across various character types.
In-the-wild Real-video Motion Transfer for Different Categories
Our method also applies to real-world videos and non-quadruped animals, demonstrating versatility across diverse scenarios.
2D-to-2D Motion Transfer
Our approach enables seamless motion transfer between videos by reconstructing articulated 3D Gaussian splats from the source video and transferring them to the target video.
Comparison With Baselines
CAMO achieves superior motion transfer quality on humanoids, quadrupeds and non-quadrupeds through direct optimization, without requiring explicit 3D supervision.
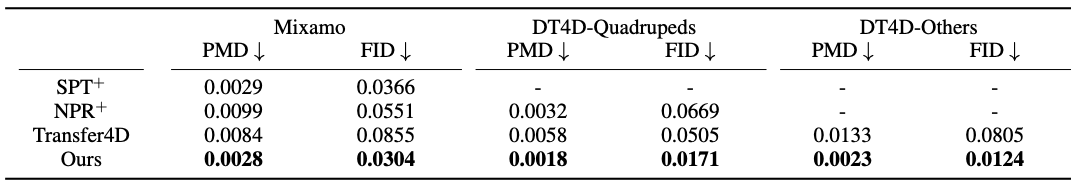
Quantitative comparison on Mixamo Humanoids and DeformingThings4D dataset.
Comparison on DeformingThings4D-Quadrupeds Dataset
Comparison on Mixamo Humanoids Dataset
Comparison on In-the-wild Real-video Scenes
Citation
@article{kim2026camo,
title={CAMO: Category-Agnostic 3D Motion Transfer from Monocular 2D Videos},
author={Kim, Taeyeon and Na, Youngju and Lee, Jumin and Sung, Minhyuk and Yoon, Sung-Eui},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2601.02716},
year={2026}
}